Both a pure astigmatism and an astigmatism in combination with another vision disorders can be corrected by EuroEyes. In order to determine whether the patient is suitable for laser surgery, a thorough consultation and a detailed preliminary examination are always carried out before the procedure. Safety and diagnostics are absolutely in the foreground during the preliminary examination. If a patient is not suitable for an eye laser correction, EuroEyes can offer other treatment methods.
Astigmatism up to 5 D
Read more
Astigmatism up to 4 D
Read more
Astigmatism up to 3 D
Read more* Depending on the thickness of the cornea ** With a very thin cornea

Implantable Toric Contact Lens (ICL) *
Astigmatism up to 6 D
Read more* Patients younger than 40-45 years

Astigmatism up to 12 D
Read more* Patients older than 40-45 yearse

连续五次收录福克斯年度医生
国际屈光外科学会(ISRS)会员
南非白内障与屈光外科学会基辛格纪念奖

拥有32年眼科临床经验
美国白内障屈光手术协会
国际屈光手术协会(ISRS)
26项发明专利[青光眼手术/葡萄膜炎/斜视/黄斑变性/结膜炎/视网膜病

德视佳眼科集团创始人
欧洲眼科医生导师
拥有35年眼科从业经历

白内障和屈光外科医生
拥有两项眼科手术专利
技术蔡司研讨会“优异演讲者”

拥有35年眼科临床经验
瑞典和欧洲科学委员会顾问
国际眼科组织的成员
多焦点晶体,ICL晶体植入(手术高度近视),激光和白内障手术的医生经验

同仁医院眼科博士
北京德视佳医疗副总监、主诊医生

中山大学中山眼科博士(眼科学)
德视佳眼科集团主诊医生

毕业于卢甘斯克州立医科大学
乌克兰眼科协会会员
曾参与瑞士SOE AAO会议
视网膜诊断,屈光手术方案制定(包含:近视,散光,白内障,老花),Yag手术等...

德视佳眼科全飞秒手术医生
上海手术机构屈光医生

蔡司全飞秒手术认证医师
北京华贸中心德视佳眼科主诊医师
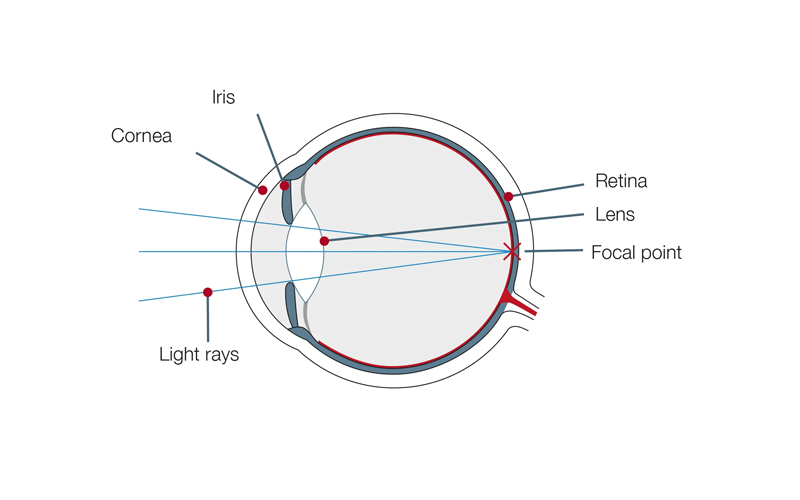
Good vision requires a sharp image being produced on the retina at the back of the eye. The optical system (cornea, crystalline lens and vitreous body) of a normal eye diverts light rays in a way that they land exactly in focus at the point of best vision on the retina, the so-called makula. This diversion of light rays is called refraction. The total refractive power is expressed in diopters (D). The total refractive power is determined on the basis of the different parts of the optical system. When the total refraction is zero diopters, objects will be depicted sharply on the retina.
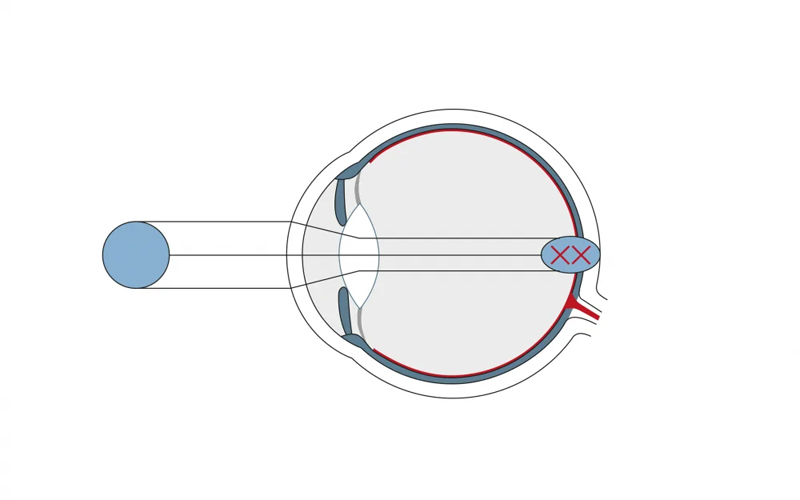
Ideally the curvature of the cornea is shaped regularly like the surface of a ball. Astigmatism occurs when the corneal surface is more an irregular shape, more like that of an egg. Instead of gathering in a single point, light focuses at several different points both in front of and behind your retina, causing blurred vision. The light is refracted differently through the different curvatures of the cornea, e.g. vertical light rays are refracted differently than horizontal ones. This results in a distorted image, and a dot may appear as a line. The optical correction is made by changing the refractive power so that the two focal points are shifted exactly onto the retina – basically the same effect as can be achieved with a toric cylindrical lens.

EuroEyes WeChat